Introduction
Email deliverability means that theemail you send actually reaches your recipient’s inbox.
It’s an essential part of every e-commerce business’s email marketing strategy. You want your promotions and newsletters to avoid the spam folder or you risk seeing your open rates plummet.
I – Understanding Deliverability
1 – The Journey of an Email
Every email—transactional, marketing, or personal—goes through at least four stages before reaching the inbox:
- It’s sent by an Email Service Provider to the mailbox provider (Gmail, Hotmail, Yahoo, Orange, etc.).
- The mailbox provider performs an initial filter, rejecting some emails such as those destined for full inboxes. These undelivered emails are called “bounces.”
- Delivered emails then go through a spam filter that checks reliability and relevance for each recipient. For example, if a recipient has already marked one of your emails as spam, future emails will likely be routed directly to their spam folder.
- After these spam filter results, the recipient receives the email in their inbox or spam folder.
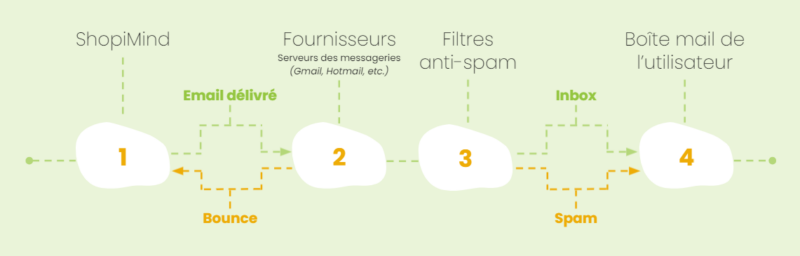
This journey takes just a few seconds or minutes depending on server locations.
ShopiMind uses servers in France and worldwide to ensure optimal delivery speed.
2 – Delivered Email Rate
Deliverability rate is often mistaken—incorrectly—for the delivered email rate. There’s an important distinction between these two statistics.
The delivered email rate refers to the number of emails sent minus those returned as bounces.
This figure includes both soft bounces and hard bounces.
These numbers are automatically calculated based on bounce notifications sent by mailbox providers. This metric does not count emails that have been redirected to spam folders.
A good delivered rate is above 95%.
 3 – Deliverability Rate
3 – Deliverability Rate
By contrast, the true deliverability rate is impossible to measure exactly since mailbox providers don’t report the number of emails sent to spam.
You can, however, estimate it using the open rates by provider.
For example: a 30% open rate with Orange and only 2% with Gmail for the same campaign likely signals a deliverability issue with Gmail—meaning this provider considers your emails as spam.
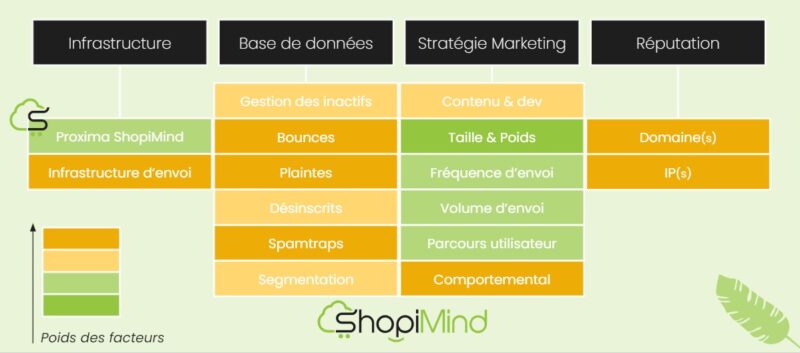
Mailbox providers base their spam filtering on multiple criteria that can be grouped into four main categories: sending infrastructure, database (destination email addresses), marketing strategy, and your domain and IP reputation.
II – Improving Your Infrastructure
For effective email campaigns, it’s essential to use secure servers suitable for mass mailing with dedicated or shared IP addresses.
These servers automate management of authentication standards like SPF and DKIM, which help providers combat identity spoofing. Bulk sends that don’t comply with these standards will not pass spam filters.
It’s also important to harmonize your domains used for sending, return, and link redirection.
ShopiMind makes it easy to set up DKIM authentication on your domain. You can also align your sending and return domains and configure redirection links to ensure your domain appears.

IP addresses are managed by the Deliverability Team, who assign senders based on different criteria.
If your domain has a strong reputation with steady, high send volumes, you may get a dedicated IP address.
If your domain is new, or if your send volume is low, making it difficult to build a reputation, you’ll use a shared server.
The more you care for your deliverability, the better the IP reputation assigned to you.
Every ShopiMind IP is monitored on a daily basis for its reputation. The Deliverability Team handles delisting management and will contact you if your IP gets blacklisted.
Our servers are optimized for email delivery and regularly updated to maintain a high-quality infrastructure.
During your email sends, the infrastructure automatically adjusts the routing speed to ensure fast delivery.

III – Nurturing Your Database
Having clean contact lists is at the core of effective communication.
There are two ways to collect your customers’ email addresses:
- Opt-in: This means getting explicit consent from a customer or visitor to send them communications—usually via a checkbox during sign-up.
- Double opt-in: This verifies sign-up by sending an automated email asking the prospect to confirm their address. This ensures the address is active and that they truly want to receive your emails. It helps keep you out of spam and boosts open and engagement rates.
Note: Opt-in is a legal requirement under GDPR, while double opt-in is recommended but optional.
Once you’ve built your contact list, keep it healthy by actively managing bounces, complaints, and unsubscribes.
We highly recommend you remove all inactive contacts—those who haven’t engaged with your emails or website for months—from your campaigns.

To simplify the management of problematic addresses, ShopiMind has automated the quarantining process for hard bounces, recipients who have complained, and identified spamtraps.
Quarantine is a dedicated list for addresses that hurt deliverability. For example, if a recipient repeatedly marks your emails as spam, their address is quarantined to prevent mailbox providers from viewing all your future emails as spam.
From your client account, you can monitor a range of metrics including deliverability stats: bounces, complaints, unsubscribes, and open rates.
IV – Sharpening Your Marketing Strategy and Reputation
Your marketing strategy is a key pillar of deliverability, especially when it comes to segmentation of your recipient lists.
Segmentation means acknowledging the differences within your audience. Someone newly subscribed to your newsletter has different needs than a customer who buys three times a month.
Better targeting your customer base with relevant content helps boost engagement (open, click, and conversion rates) while also reducing complaints.
Segmentation therefore has a major impact on your reputation. Once you’ve segmented, you can easily adjust sending volume and frequency to build consistency.
Once you’ve segmented, you can easily adjust sending volume and frequency to build consistency.
This adjustment should be based on your own metrics: delivered email rate, bounce rate, open rate, click rate, unsubscribe rate, complaints (spam reports by recipients).
There’s a difference between emails that go directly to spam and those that reach the inbox but are later moved to spam or reported by recipients.
The first group is not detectable, but the second is. You can find this data in your client account in the “Statistics” tab under “Spam.”
Note: An email that follows design and content best practices is more likely to bypass spam filters and get opened by recipients. ShopiMind is preparing an article dedicated to optimizing your marketing email content—coming soon!
Every sender can tailor their marketing strategy to their audience. ShopiMind also offers a comprehensive audit service to check the effectiveness of your campaigns. On request, we can examine your content, targeting, and segmentation to offer you personalized recommendations.

Additionally, our Deliverability Team uses a full suite of reputation tracking tools, so they can alert you quickly if any unusual results are detected.
Conclusion
You now have all the tools you need to optimize your deliverability. By fine-tuning your campaigns and tracking your results, you will steadily grow your open rates.
Since your open rate has a direct impact on your click rate, you’ll see why deliverability is closely linked to your return on investment.
Now it’s your turn!
About the Author
As Deliverability Manager at ShopiMind, Béranger comes from a web background. He started out as an email developer before quickly specializing in deliverability.
For the past 8 years, he has developed expertise and deep understanding of email marketing filtering rules.
His two main missions are to guide you in email marketing best practices and optimize technical infrastructure to ensure top deliverability.
Glossary
Deliverability: Deliverability refers to the moment when the email lands in the recipient’s inbox.
Domain name: A unique name identifying an individual or organization online, so you don’t have to memorize or re-type a long IP address. It’s like a postal address, but for the web.
IP: The identification number for every device connected to a network using the Internet protocol. In this article, we focus on the sending IP for your newsletters and mailings.
Mailbox provider: Email hosting service that offers users servers for sending, receiving, accepting, and storing email from other organizations or users.
Bounces: Emails that fail to reach the recipient’s inbox—usually because the address doesn’t exist or the inbox is full.
Related Articles
Boosting your average order value is one of the most [...]
Email marketing is an incredibly effective marketing tool for every [...]


